by Venchito Tampon | Last Updated on May 19, 2025
You’re now part of talent development, ready to launch leadership training for your new and seasoned employees. What you need the most is the best leadership training topics to discuss in corporate training.
In this guide, I’ll discuss the key leadership training topics that build essential skills. Whether leading a small team or a large organization with thousands of employees, you must hone and nurture specific skills to produce better outcomes and long-term success.
Contents
Toggle1. Adaptability and Resilience
In the age of AI and technology, leaders are facing a strong wave of innovation that a person with adaptability and resilience can stay effective during change and uncertainty.
These skills alone can help them endure and handle crises (which we have experienced so far during the COVID-19 season). They can also help their team members recover from setbacks by leading by example.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Building a Change-Ready Culture
Knowledge: Organizational change principles, change management theories
Skills: Communication, change facilitation, employee engagement
Attitude: Openness to change, flexibility, proactive mindset
Insights: Change management, in general, is an advanced skill in leadership training for managers and supervisors. If leaders are trained with the fundamentals of leadership and management, and they’ve been demonstrating behaviors and skills as more than the above leaders, change management is the next level they should consider advancing in terms of competence.
2. Fostering a Growth Mindset
Knowledge: Principles of neuroplasticity, continuous learning models
Skills: Encouraging feedback, challenging fixed beliefs, personal development
Attitude: Positive outlook, willingness to learn, perseverance
Insights: Changing mindsets in leadership training requires specific activities that encourage self-reflection instead of lecture-based learning. Industry professionals can learn more from reflecting on and discussing events with other participants. As a corporate leadership trainer, this has been my go-to learning structure for fostering a growth mindset in leaders.
3. Identifying Opportunities and Threats
Knowledge: SWOT analysis, risk assessment methods
Skills: Critical thinking, strategic planning, scenario analysis
Attitude: Risk-awareness, forward-thinking, adaptability
Insights: SWOT analysis is a good way to spot opportunities and threats in your current role, team, and department. This is typically done before the year starts. However, you shouldn’t limit the exercise to just leadership training proper. You can also integrate it into your monthly or weekly tasks, as it can help you be more aware of your strengths and weaknesses – truly upskilling yourself.
4. Recovering from Setbacks
Knowledge: Resilience frameworks, coping mechanisms
Skills: Emotional regulation, stress management, problem-solving
Attitude: Perseverance, confidence, optimism
Insights: In previous leadership training programs, topics like recovering from setbacks were not commonly seen. Today, it has become a core topic of leadership training, and we even have a standalone training for this skill area. The reason is that a considerable number of professionals are still recovering from their losses (and potentially having mental health issues) that need to be addressed so they can be more equipped to face present and future challenges.
2. Change Management
As mentioned earlier, change management is an advanced skill for leaders. As a corporate trainer, I see it as a core corporate training program initially suited for mid-level, top-level, and suite-level managers. However, a couple of years later, it became part of the training development curriculum for aspiring and new managers.
The primary reason is that change management applies to superiors at the top and leaders who are still part of the front-line team, facing challenges at work head-on. If they know how to solve problems, it could have a significant impact upwards, and it can help drive innovation by bringing creative ideas that only front-line managers can think of.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Understanding Change Processes
Knowledge: ADKAR model, Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
Skills: Planning, communication, execution
Attitude: Patience, adaptability, resilience
Insights: I’ve had good change management training for strategy managers in one of the top outsourcing companies in the Philippines. It was a great experience learning directly from strategy managers who experience drastic changes inside and outside the organization (technology adaption, tools, strategies, etc..). They crafted their own change management process from my given framework, and a good couple of hours discussing their real-life examples of changes allowed them to increase their self-awareness and individually create their action plans to tackle them.
2. Managing Resistance to Change
Knowledge: Psychological reactions to change, stakeholder management
Skills: Negotiation, conflict resolution, persuasion
Attitude: Empathy, persistence, strategic thinking
Insights: The ADKAR and Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model are the best frameworks for change management. They’ve been tested and practiced across different organizations and industries, giving you the confidence that it works and would impact your target participants similarly.
3. Developing Employee Career Paths
Knowledge: Talent development strategies, mentorship techniques
Skills: Coaching, career mapping, performance assessment
Attitude: Supportiveness, vision-oriented thinking, encouragement
Insights: This competence addresses the human resource (human capital, as others refer to it) or any department involved in talent development. Change management today also includes drafting and implementing a solid career map for employees. It upskill HR leaders to consider the changes in job roles as changes arise in the organization.
3. Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching and mentoring have become a buzzword today. Still, I see few companies invested in leadership development (most companies with this as a core topic for leadership training are multi-national companies, but still very few).
Coaching and mentoring are essential skills in driving individual work performance. Leaders can help their direct reports see themselves as performers and address performance gap issues.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Active Listening
Knowledge: Listening techniques, barriers to effective listening
Skills: Paraphrasing, asking clarifying questions, non-verbal cues
Attitude: Patience, attentiveness, empathy
Insights: Active listening isn’t just a particular behavior but a skill that leaders should constantly practice and master to improve. To encourage participants to practice this skill, you should design the training program to include workshops that enhance active listening. You should also probably share additional principles and points on mastering active listening.
2. Feedback and Reflection
Knowledge: Feedback models (e.g., SBI, GROW)
Skills: Constructive criticism, performance evaluation, goal setting
Attitude: Objectivity, encouragement, continuous improvement
Insights: Giving feedback is one of the leadership conversations that can help leaders’ subordinates improve their day-to-day work. Opportunities are spotted to put strengths into practice and identify gaps at work—in terms of knowledge, skills, and behavior- and improve each to increase the level of competencies.
4. Conflict Resolution
Conflicts are part of handling teams. As you transition teams from forming (the first stage of team development) to norming (the second stage), you’ll experience and see actual conflicts between team members that either challenge them to grow or could be a barrier to team harmony and productivity.
Knowing how to handle disputes effectively can help your team grow and function better.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Identifying Sources of Conflict
Knowledge: Workplace conflict types, conflict resolution models
Skills: Root cause analysis, mediation, active listening
Attitude: Fairness, open-mindedness, emotional control
Insights: It’s a separate fundamental skill to know the root cause of the conflict. And it is easier said than done because you must figure it out honestly and critically during discussions and open forums.
2. Mediation Skills
Knowledge: Interest-based negotiation, neutral facilitation techniques
Skills: Compromise strategies, impartial listening, persuasion
Attitude: Neutrality, respect, solution-driven mindset
Insights: Your goal as a leader is not to be one-sided. You aim to unite parties involved using active listening skills and specific values such as respect and neutrality. The higher you go up the corporate ladder, the more challenging it is to manage subordinates’ disputes.
5. Effective Communication
All leaders are communicators. It is only a matter of whether the communication has a positive or negative impact. If you can persuade people with words and actions through effective communication, you can inspire them to achieve individual and team goals.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication
Knowledge: Communication models, body language interpretation
Skills: Public speaking, storytelling, engaging presentations
Attitude: Confidence, approachability, authenticity
Insights: Most of how you show it is what your subordinates pick up as the message of your communication. This includes your tone of voice, speed, dynamics, and body language that you may not be consciously aware of as you speak but highly dictates how your team members perceive your message.
2. Active Listening
Knowledge: Barriers to effective listening, techniques for engagement
Skills: Summarizing, clarifying, showing empathy
Attitude: Open-mindedness, patience, attentiveness
Insights: Active listening is an essential element in leadership communication. By listening to them right away, you understand better the intent behind every word they say. This impacts your response to every situation and allows you to garner and build more trust with your team members.
6. Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence has become a core module for many corporate training programs. Not only is it necessary for anyone to manage their emotions, but it’s also apparent that people are sensitive to other people’s emotions—a crucial area in strengthening work relationships.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Self-awareness and Self-Regulation
Knowledge: Emotional intelligence models, mindfulness techniques
Skills: Emotional control, stress management, decision-making
Attitude: Reflectiveness, calmness, adaptability
2. Empathy and Social Awareness
Knowledge: Cross-cultural communication, emotional recognition
Skills: Perspective-taking, conflict resolution, inclusivity
Attitude: Compassion, fairness, open-mindedness
3. Relationship Management
Knowledge: DEI principles, interpersonal dynamics
Skills: Building trust, managing teams, networking
Attitude: Empathy, inclusivity, approachability
Insights: These three components of emotional intelligence—self-awareness, empathy, and relationship management are areas where one can master and strengthen competencies. I see these three pillars in most emotional intelligence frameworks, including Daniel Goleman’s Four Domains of Emotional Intelligence.
7. Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
We face problems and make decisions every single day at work. Leaders who know how to develop the best possible solution for every problem will have higher chances of getting promoted and achieving the organization’s best performance.
Problem-solving and decision-making training can elevate your leaders’ critical and creative thinking skills, making them more competent and confident at work.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Critical Thinking
Knowledge: Logical reasoning, bias recognition
Skills: Evaluating evidence, analyzing data, root-cause analysis
Attitude: Skepticism, curiosity, patience
2. Decision-Making Frameworks
Knowledge: SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis
Skills: Risk assessment, prioritization, scenario planning
Attitude: Confidence, responsibility, ethical considerations
Insights: In my problem-solving decision-making training, I teach the framework of SAPADAPPA, which is a PSDM tool to help leaders come up with the best solutions by first analyzing their situation, getting to the root cause of their problems, identifying the probable reasons and coming up with the best solution using the decision analysis.
8. Team Building and Collaboration
While there are many team-building facilitators, it is also true that leaders must know how to build their teams, not necessarily have them play different activities. But beyond just playing games, it is more about leaders intentionally developing their teams.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Trust and Psychological Safety
Knowledge: Team dynamics, trust-building techniques
Skills: Transparency, delegation, recognition
Attitude: Honesty, openness, inclusivity
Insights: Psychological safety is a keynote talk or panel discussion topic in many HR and talent development seminars. The entire premise revolves around creating a healthy culture where employees are more open to their ideas, concerns, and challenges, which is a strong indicator of such a culture.
2. Effective Collaboration
Knowledge: Group problem-solving models, facilitation techniques
Skills: Conflict resolution, role assignment, active participation
Attitude: Cooperation, commitment, mutual respectf
9. Time Management
Effective time management helps leaders allocate their resources properly—where the most expensive resource every leader should manage is their time.
Leaders are not only individual contributors but also invest time in coaching and supporting their subordinates, learning to achieve maximum productivity while maintaining healthy relationships with the team members. These are crucial in today’s working environment.
Key Competencies and KSA Requirements
1. Prioritization and Planning
Knowledge: Time management frameworks (Eisenhower Matrix, Pomodoro Technique)
Skills: Scheduling, goal setting, workload distribution
Attitude: Discipline, consistency, self-motivation
2. Reducing Distractions and Increasing Focus
Knowledge: Productivity techniques, cognitive load management
Skills: Task batching, setting boundaries, focus improvement
Attitude: Commitment, awareness, persistence
How to Determine Leadership Training Topics?
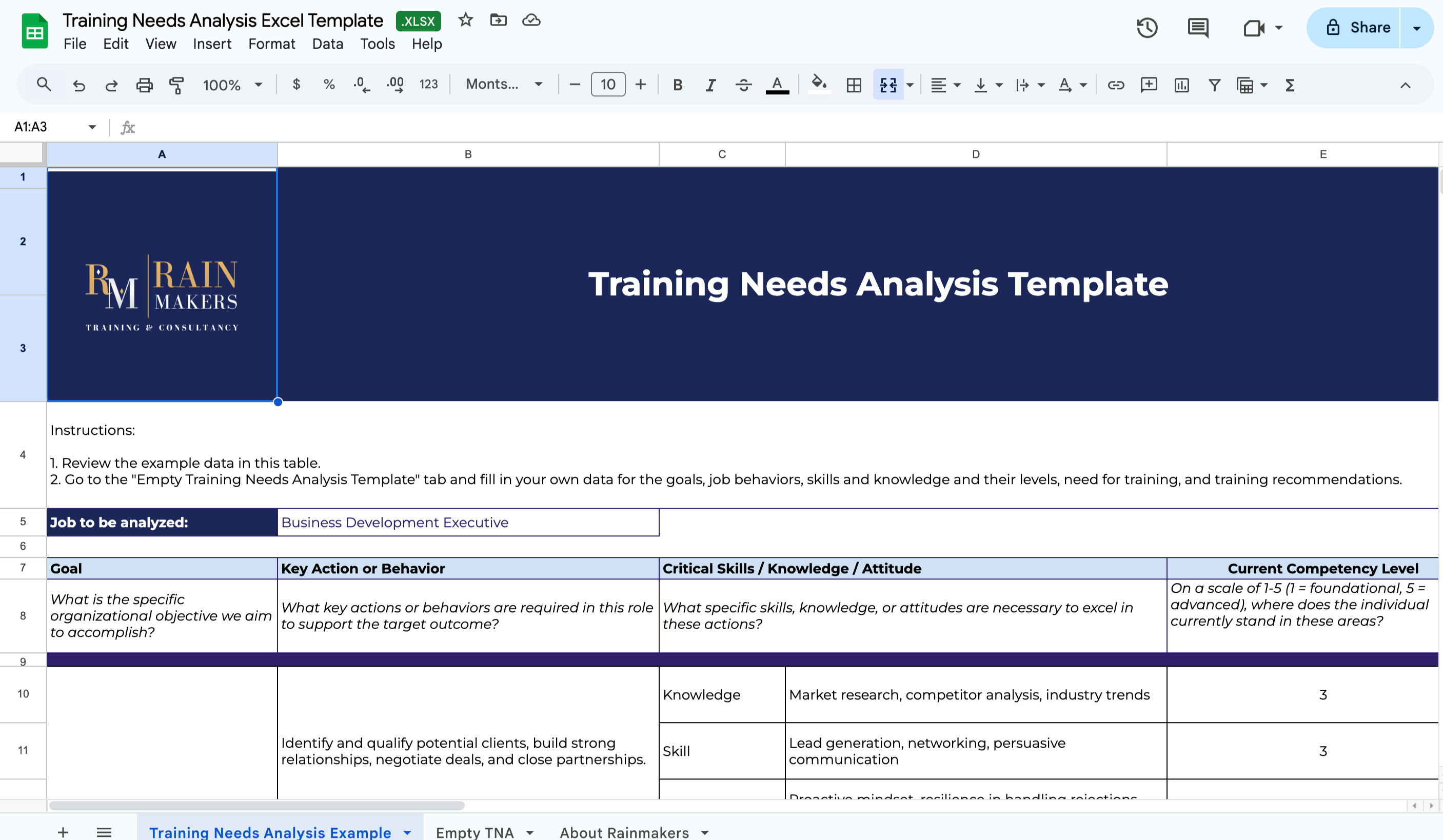
1. Conduct a Training Needs Analysis
A Training Needs Analysis (TNA) identifies gaps in leadership competencies. A structured assessment evaluates employees’ current skills, knowledge, and attitudes.
You can check out our Free Training Needs Analysis Template.
2. Identify Problem and Growth Gaps
As you go deeper with your training needs analysis, you’ll find both problem and growth gaps in the competencies of your subordinates. This is where you need to analyze them so you can design a training program (or outsource it to the best corporate training provider in the Philippines – if you lack the resources to do so).
What’s the difference between the two: problem gaps and growth gaps?
Problem Gaps: These indicate a deficiency in key leadership competency, such as ineffective communication.
Growth Gaps: These focus on continuous development, ensuring employees refine their skills without pressing issues.
3. Design and Align Training with Business Goals
All leadership training must support organizational objectives (aligned leadership training objectives). It doesn’t stand alone like another statistic or schedule in the training calendar.
Leadership training programs are investments in the company’s people, so it’s critically important to make them worthwhile in terms of costs and time.
4. Ask for Recommendations From SMEs or Trainers
You can hire a training design consultant if you lack the technical knowledge or expertise to identify your employees’ training needs. These consultants specialize in analyzing and designing aspects of a corporate training program (end-to-end), giving you everything you need to create a successful training event.
5. Use Proven Frameworks
If you want to do it yourself, you can go directly to widespread and successful leadership training frameworks for the above leadership competencies
- Change Management: ADKAR Model
- Communication: DISC Model
- Emotional Intelligence: Goleman’s EQ Model
- Decision-Making: SWOT & Cost-Benefit Analysis
If you’re looking for an engaging leadership training program that meets your training needs and business objectives, contact us today for a free quote.
The Author
Venchito Tampon
Venchito Tampon is a Filipino motivational speaker, Business Consultant, Founder and Lead Corporate Trainer of Rainmakers Training Consultancy. He trained and spoken in over 250+ conventions, seminars, and workshops across the Philippines and internationally including Singapore, Slovakia, and Australia. He has worked with top corporations including SM Hypermarket, Shell, and National Bookstore.
He also founded SharpRocket, a digital marketing company, Blend N Sips, eCommerce for coffee supplies, and Hills & Valleys Cafe, a local cafe with available franchising.
He is a certified member of The Philippine Society for Talent Development (PSTD), the premier organization for Talent Development practitioners in the country.
An active Go Negosyo Mentor (of Mentor Me program) and a business strategist and consultant.
You may also like
Best Leadership Training Providers in the Philippines [2026]
If you’re short on time: After evaluating 15+ corporate training providers in…
Leadership Training Guide Philippines in 2026: Types, Programs, and Providers
Leadership training in the Philippines continues to grow as organizations…